Revolutionizing the Science of Virus-Like Particles
Working Together With the Human Body’s Powerful and Innate Defense Against Disease – the Immune System
When properly stimulated, the human immune system is incredibly powerful and has profound potential. Because of their structural similarity to viruses presented in nature, including their particulate nature and repetitive structure, virus-like particles (VLPs) are ideal for stimulating potent immune responses.
VBI’s portfolio includes vaccines and immunotherapeutics derived from three variations of VLP technology platforms – VLPs, enveloped VLPs (eVLPs), and mRNA-launched eVLPs (MLE).
Virus-Like Particles (VLPs)
- Sub-unit vaccines with no infectious material
- VLPs mimic the natural presentation of viruses
- Only a few antigens self-assemble into orderly VLP structures – notably, this includes the hepatitis B antigens
Enveloped Virus-Like Particles (eVLPs)
VBI’s eVLP platform technology expands the list of potentially-viable target indications for VLPs by providing a stable core (Gag Protein) and lipid bilayer, which is the natural way these antigens are presented to the immune system.
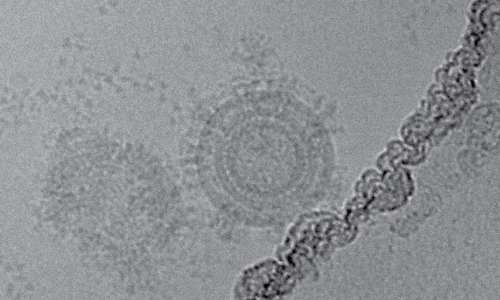
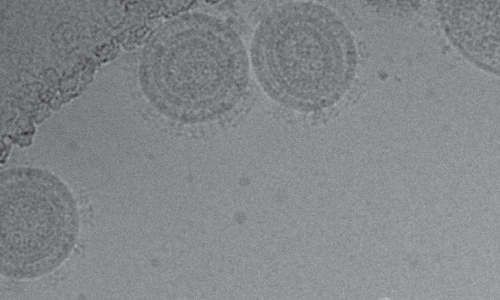
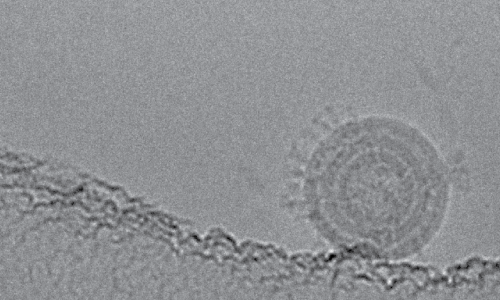
Electron microscopy images of VBI’s eVLP-derived CMV Vaccine Candidate, captured at The Scripps Institute.
Highly Immunogenic
Elicit immune responses comparable to, or better than, natural infection by closely mimicking the structure of the target virus
Flexible and Customizable
Ability to rationally design a vaccine or therapeutic by including different antigens and controlling their relative expression
No Infectious Material
Clinical study data suggest eVLPs have a clean safety profile, and with no infectious material they cannot revert to an infectious state
In contrast to standard mRNA vaccines that transport genetic code to cells within a lipid nanoparticle, which instructs the immune system to generate proteins that trigger an immune response to a target antigen, VBI’s eVLP vaccines are delivered to the body in the form of particles that have been created ex vivo, in bioreactors. These particles mimic the natural conformation of viruses, activating a potent, natural immune response.
However, VBI has also developed a technology that leverages the strengths of both eVLP and mRNA technologies…
A Novel Approach to Particulate Vaccines :
mRNA-Launched eVLPs (MLE)
The addition of genetic code for a particle-forming structural protein – the same protein at the core of VBI’s eVLPs – to an mRNA vaccine fundamentally changes cellular interaction with the vaccine.
The addition of this protein instructs cells to not only create target antigens but to also create eVLPs in vivo. These particles are released from the cells that generate them to circulate in the body, provoking the immune system to drive potent B-cell and T-cell responses.
In addition to the benefits seen with VBI’s eVLP platform technology, the MLE platform also demonstrates:
Potent Functional Immunity
- Elicits enhanced functional neutralizing antibodies
- Induces generation of polyfunctional CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses
Fast Manufacturing & Customizable Design
- Fast manufacturing timelines – similar to other known mRNA vaccine production platforms
- Building upon flexibility of eVLP platform, target antigens can be expressed both internally and externally
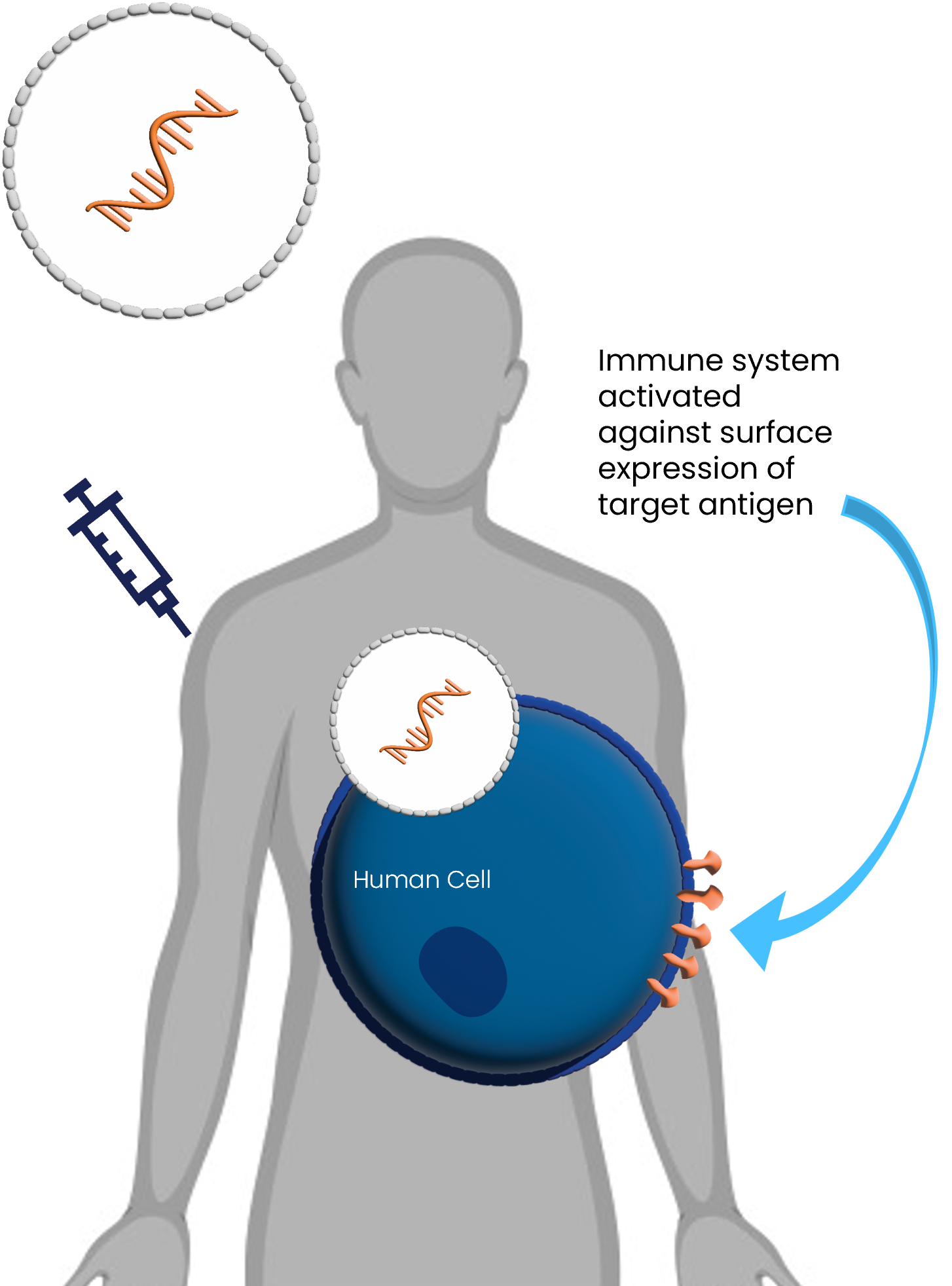
Standard mRNA Vaccine
- Target proteins are expressed on surface of human cell
- Immune response attacks these proteins – making healthy human cells their target
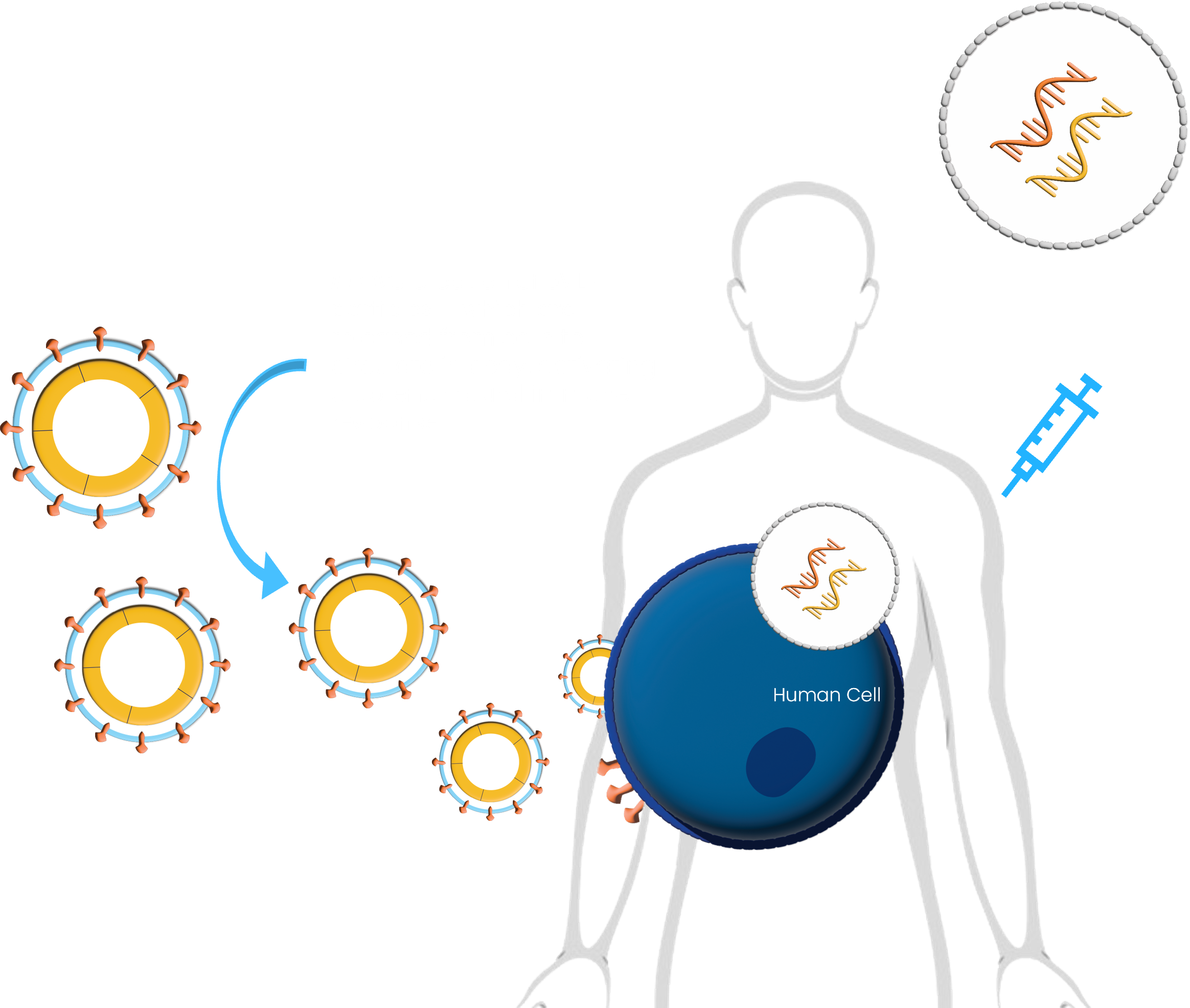
MLE Vaccine
- Addition of particle-forming mRNA instructs cells, in vivo, to produce eVLPs that will express target antigens
- This process is nearly identical to the way that viruses replicate in nature – though MLE do not contain infectious material
- Natural circulation of eVLP particles promotes more potent B-cell and T-cell activation
Learn More About eVLPs
VBI’s Chief Scientific Officer, Dr. David E. Anderson, Ph.D., discusses VBI’s unique approach to vaccine development.